State-dependent inhibition of GABA receptor channels by the ectoparasiticide fluralaner
Release time:2021-12-20 10:06:00
Highlights
• Fluralaner, an isoxazoline ectoparasiticide, potently inhibits GABARs.
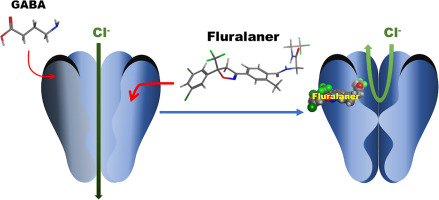
• Inhibition by fluralaner progresses over time after every GABAR activation.
• Fluralaner does not inhibit the GABA response in the GABAR resting state.
• Fluralaner hardly dissociates from the binding site upon GABAR activation.
Abstract
γ-Aminobutyric acid (GABA) receptors (GABARs) are ligand-gated Cl− channels, which cause an influx of Cl− that inhibits excitation in postsynaptic cells upon activation. GABARs are important targets for drugs and pest control chemicals. We previously reported that the isoxazoline ectoparasiticide fluralaner inhibits GABA-induced currents in housefly (Musca domestica) GABARs by binding to the putative binding site in the transmembrane subunit interface. In the present study, we investigated whether fluralaner inhibits the GABA response in the GABAR activated state, the resting state, or both, using two-electrode voltage clamp electrophysiology protocols. We found that inhibition progresses over time to steady-state levels by repeated short applications of GABA during fluralaner perfusion. The GABA response was not impaired by fluralaner treatment in the GABAR resting state. However, once inhibited, the GABA response was not restored by repeated applications of GABA. These findings suggest that fluralaner might reach the binding site of the activated conformation of GABARs in a stepwise fashion and tightly bind to it.
Graphical abstract
References:
https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S004835752100239X